Graham Speight, Giulia Poloni, Natalie Milner, Venu Pullabhatla, James Reid, Jolyon Holdstock, Lyudmila Georgieva (Oxford Gene Technology)
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a chronic lymphoproliferative disorder characterized by monoclonal B cell proliferation. It is the most common adult leukemia in Western populations and comprises 25 to 30% of leukemias in the United States.
A wide variety of genomic variations are associated with CLL, ranging from single nucleotide variants (SNVs) and insertions/deletions (indels) to complex chromosomal rearrangements such as copy number alterations (CNAs) of part or whole chromosome. Chromosomal abnormalities are very common in CLL, the most frequent being del(13q), trisomy 12, del(11q), del(17p) and del(6q).
Comprehensive genetic research into CLL requires multiple testing strategies with high associated costs. In this study, we tested the capability of OGT’s NGS panel, SureSeq™ CLL + CNV V3, to detect SNVs and indels as well as chromosomal aberrations in CLL research samples, allowing for the detection of CLL variants in a cost efficient and timely manner.
The SureSeq hybridization-based enrichment approach and OGT’s Universal Complete NGS Workflow Solution were used throughout this study (Figure 1).
For each set of 8 samples, one Reference DNA (negative for aberrations in the critical regions) was hybridized and sequenced with the research samples. Information from reference DNA samples are used in the analysis for CNAs detection.
Sequencing was conducted using 2 x 150 bp reads on an Illumina MiSeq® V2 300.
The workflow and the panel were tested on reference DNA (Coriell Institute, Horizon) to validate the overall performance. CNAs capability was demonstrated by using 21 research samples with known CNAs in the regions of interest previously characterized by FISH.
To mimic CNAs at low tumor content, 11 research samples with known aberrations were diluted in order to create CNA carriers with 20-40% tumor content.
Sequencing data analysis including CNA detection was performed using OGT’s Interpret NGS Analysis Software.
Data presented here are from 21 research samples that were processed using the OGT workflow in combination with OGT’s Interpret NGS Analysis Software.
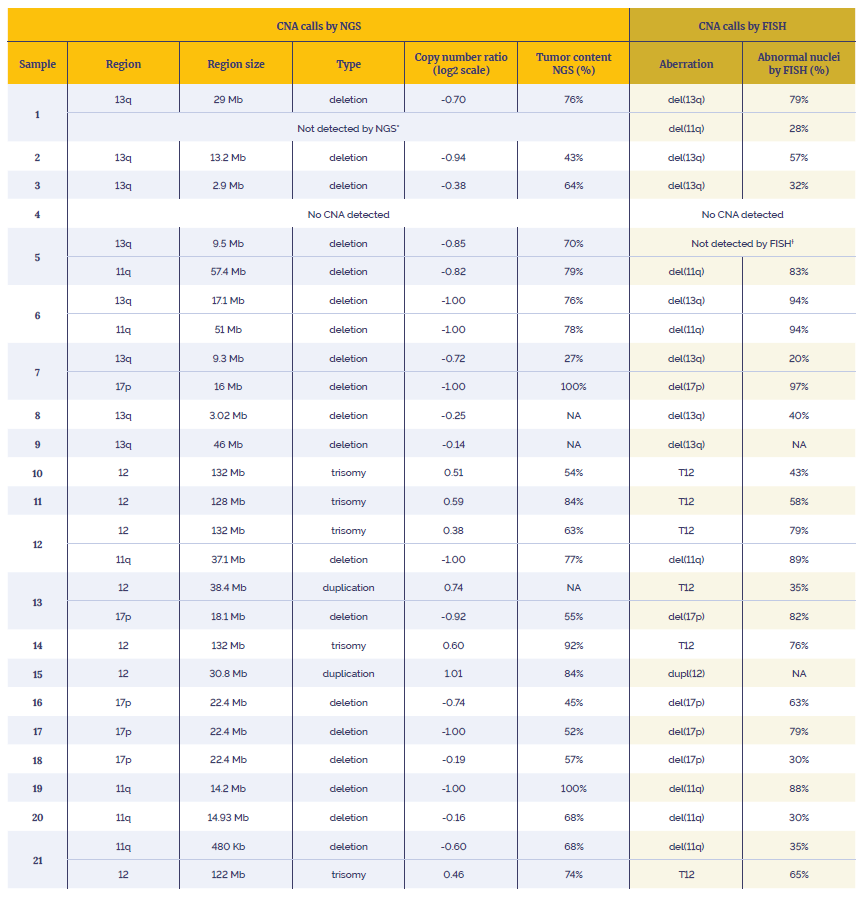
Table 3: Data generated using the SureSeq CLL + CNV V3 Panel in combination with the OGT’s Universal Complete NGS Workflow and OGT’s Interpret NGS Analysis Software.
*Not enough material to perform orthogonal tests. Suspected over-estimation of tumor content by FISH, likely to be below the level of detection of the assay (20%).
†Not enough material to perform orthogonal tests. Highly confident variant, log2 ratio=-0.85.

SureSeq: For Research Use Only; Not for Diagnostic Procedures.
Call +44 (0)1865 856800 Email contact@ogt.com
Send us a message and we will get back to you